The recent news about Google beginning to implement the end of third-party cookies has left many in the industry pondering the future of online businesses.
This move, which was announced in 2021, finally began to be implemented on January 4, 2024, with cookies initially being disabled for 1% of Chrome users.
This change represents a significant challenge for marketers who have traditionally relied on third-party cookies to collect data about their audiences and target advertising campaigns.
Let’s take a closer look at what we’re talking about, how cookies work and what you can do as a marketer!
Speaking of cookies: what exactly are they?
Cookies are fundamental elements in web browsing and can be classified according to their origin, temporality and function. In short, there are two main types of cookies:
- Own cookies: these are generated directly by the website being visited and are used to improve the user’s browsing experience on that specific site. These cookies are downloaded to the user’s computer and are managed internally by the website.
- Third-party cookies: they come from external servers and are not generated by the site being visited. These cookies may be used by social media platforms or other services to track users’ online activity and display personalized advertisements.
The difference between first-party and third-party cookies is based on who creates them and how they are used on websites. To understand this, we must first understand how web communication works.
When we visit a website, our browser makes a request to the site’s web server using the HTTP protocol. This request includes the URL of the site we want to access. The server responds to this request by sending the data necessary to load the web page in our browser. This process is characterized by being stateless, which means that each request is independent and has no previous history.
This is where cookies come into play: although each HTTP request is independent, third-party cookies allow companies and advertisers to track the user across multiple sites and collect information about their online behavior.
Although each HTTP request is independent, third-party cookies allow a kind of “continuity” in tracking the user across different websites, to collect information about their behavior and to be able to personalize their experience.
So, we can say that not all cookies are bad. While first-party cookies are created and used by the website we are visiting itself and are necessary to have an overall view of the user’s behavior, third-party cookies are created by other sites and are used to track the user’s activity on various websites.
Why kill third-party cookies?
If we’ve always used them, what’s happening now and why does Google want to block them?
These cookies have been a fundamental tool for tracking user behavior and delivering targeted ads for decades in digital marketing. In fact, blocking third-party cookies does not benefit Google or other players in the advertising industry. Third-party cookies drive Google’s advertising business – Google Ads, for example, is responsible for more than 80% of the tech giant’s revenue.
However, due to growing concerns about privacy and security of user data, major web browsers, including Google Chrome, have announced plans to phase out support for third-party cookies.
Google has announced this change as part of its efforts to address user privacy concerns and promote a more secure and transparent ecosystem.
To better understand the threat posed by third-party cookies, we want to explain their disadvantages.
What’s behind Third-Party Data
Although cookies are necessary to track user behavior on a website, we tell you all the disadvantages of Third-Party Data and the danger they represent today in the digital world:
- Sale of user data: one of the main disadvantages of third-party cookies is that the data collected can be sold to third parties without the user’s consent. This raises concerns about the privacy and security of user data, especially when it comes to financial and purchasing information.
- Lack of user awareness: many users browsing online are unaware that their data is being collected and shared through third-party cookies while browsing and shopping.
- Potential security breaches: Third-party cookies can pose a risk to the security of user data if not handled properly. Cookies can be vulnerable to hacker attacks and data theft, which can compromise users’ personal information.
- Data reliability: a significant disadvantage of third-party cookies is the unreliability of the data collected. Often, companies are more interested in financial gain than in data accuracy. This can lead to the sale of data that is not completely accurate or truthful. For example, companies may collect demographic information that is incorrect or based on assumptions, which can affect the effectiveness of marketing and personalization strategies.
- Risk of misprofiling: the collection and sale of data through third-party cookies may result in the creation of incorrect or biased profiles of users. This can lead to discrimination in product offerings, pricing or offers based on incorrectly identified demographic characteristics or purchasing behavior.
While it is true that to date eCommerce has used third-party data to provide users with a more personalized and optimized online experience, the time has come to rethink the way this data is collected by leveraging new technologies in the market.
The “end of cookies” does not represent the end of data collection, nor does it mean that from now on eCommerce will have no way to track and understand user behavior: this is a key moment to start thinking about new ways to obtain more reliable and accurate data.
The potential of First-Party Data
First-party data, or first-party data, is information collected directly from users by a company. Unlike third party data, first-party data comes from direct interaction with customers and website visitors.
It works as follows:
- Direct collection: first-party data is obtained through direct interaction between users and online companies. This may include actions such as registering accounts, making purchases or participating in surveys, among others.
- Relevant and voluntary information: information collected as first-party data is provided voluntarily by users. This means that users are aware of what information they are sharing and for what purpose. For example, when subscribing to an eCommerce newsletter, users may consciously and deliberately provide their name, email address and product preferences.
- Improving user experience: once collected, first-party data is used to better understand customers and improve their experience on the website itself. This means that companies know exactly how users behave within their website. In this way, they can personalize product recommendations, send relevant offers and promotions, and improve site navigation by adapting to each user’s individual preferences.
First-party data is an invaluable tool for eCommerce, as it allows them to better understand their customers and deliver personalized and relevant experiences, using truly reliable and accurate data, as it is obtained directly from the source. In addition, by prioritizing privacy and transparency in data collection and use, companies can comply with privacy and data protection regulations, such as GDPR in the European Union and CCPA in the United States, avoiding regulatory fines and penalties.
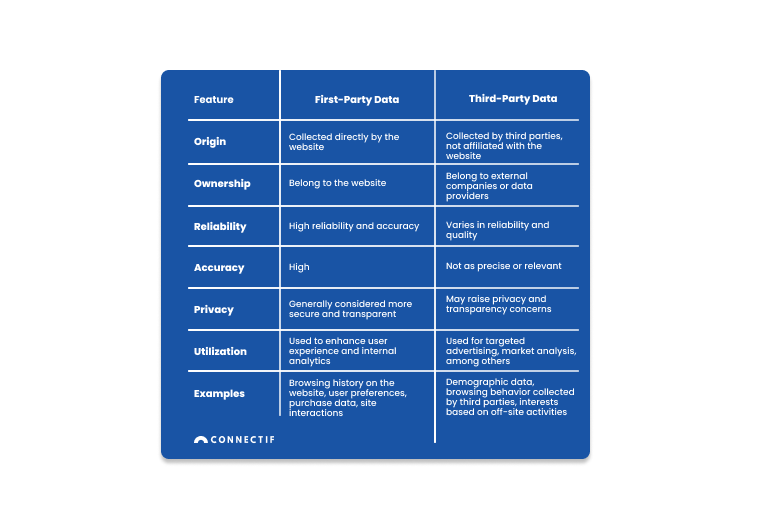
Main differences between First-Party Data and Third-Party Data
We are now going to show you a detailed comparison between First-Party Data and Third-Party Data in the context of eCommerce and online data collection.
We examine several key aspects, such as data origin, ownership, reliability, accuracy, privacy and data usage. By understanding these differences, you will be able to determine what type of data will provide a better user experience and target specific marketing strategies on your website based on your business objectives.
What happens next?
Now that we are facing new changes, we know that, as a marketer, adapting can be challenging. However, here’s some valuable advice: rely on First-Party Data. This data is incredibly accurate, as it is based on specific user interactions on a website.
In this blog post, you’ll dive into how Connectif handles this First-Party Data and explore all that our clients have achieved over the years thanks to the power of the Data First approach. You’ll also find:
- A detailed explanation of what first-party data is and why it is crucial in today’s landscape.
- The many advantages First-Party Data offers, highlighting its accuracy and reliability.
- Real-world examples of how the use of first-party data has transformed marketing strategies and driven sales in our clients’ eCommerce.
Get now a deeper understanding of how First-Party Data can be the best ally for your eCommerce. Join us on this journey to discover how to become a Data First marketing superhero – don’t miss out!




